Linked Wearables
Table of Contents
- Introduction
-
Linked Wearable
- Creating a Linked Wearable Collection
- Creating Linked Wearables one by one
- Creating Linked Wearables in bulk
- Seeing the wearables in world
- Editing the collection name
- Editing the collection ID or URN
- Deleting the collection
- Editing a single wearable
- Editing a wearable’s ID or URN
- Editing wearables in bulk
- Submitting your Linked Wearables
- Building the API
- Closing up
Introduction
About
In accordance with the initial DAO proposal for Linked Wearables (previously called: Third Party Wearables) and the last approved Draft Proposal with final definitions, this document will serve as documentation to cover all the relevant details around the Linked Wearables feature.
This document is mostly oriented for representatives of Third Parties that want to give their communities the ability to wear their NFTs as wearables when strolling through Decentraland.
What are Linked Wearables?
Linked Wearables are 3D representations of NFTs that originate from outside Decentraland that can be used as wearables in-world, can be equipped on the avatar, and are found in the backpack.
Linked Wearables are not regular wearables. They look the same, but carry a completely different meaning.
Linked Wearables do not exist inside traditional wearable collections, have no rarity, and can not be sold in primary or secondary markets. They are only in-world representations mapped to external NFTs by a Third Party.
Imagine that you have an NFT project called ‘Cryptojackets’ where every NFT is a different kind of 2D jacket and you want your users to have a 3D representation of their jacket in their Decentraland backpack. Linked Wearables will allow you to submit 3D representations of your NFTs inside Decentraland. There is no need to mint a new token, and your current NFT project will have a new out-of-the-box feature to offer!
Costs
It’s free! Yes. Converting your NFTs in to Linked Wearables is free for all Third Parties that were approved by the DAO (4M VP).
Even though there is a storage cost to upload the 3D representations of your Linked Wearables and a cost for the Curation of your 3D models, the DAO will cover these fees in order to encourage new communities to bring their NFTs to Decentraland!
Getting started - DAO Proposal
The first step to registering your NFTs as Linked Wearables is to be admitted by the DAO as an enabled Third Party (the original creator of the external NFT) by submitting a proposal using the template in the new category “Linked Wearables Registry”.
Third Parties will need to share details about their project, collection, and define the managers that will later upload the 3D models of their NFTs in the Builder.
The passage threshold to become approved is 4 million Voting Power and the Voting Period is 1 week. Resubmission is allowed.
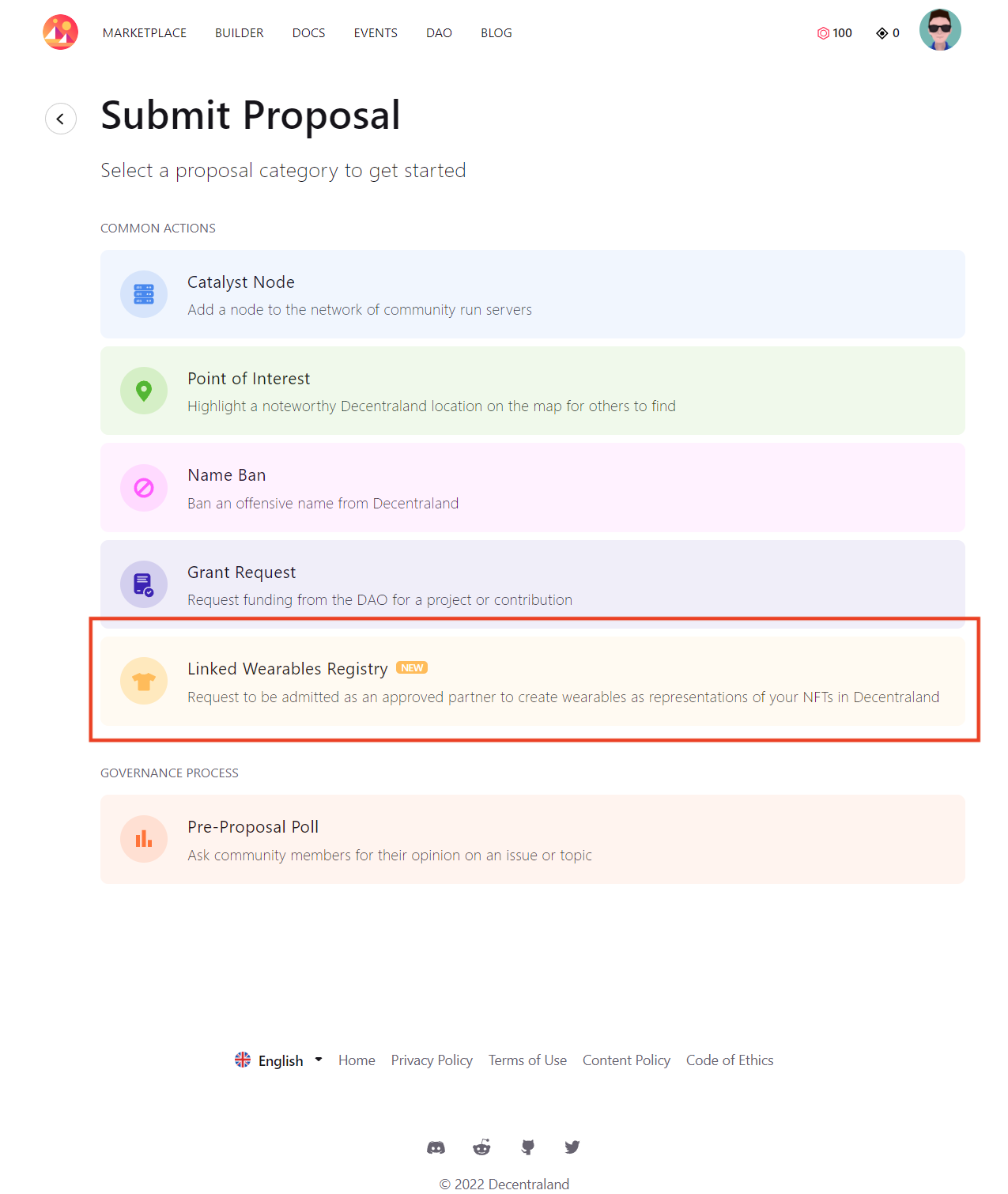
After the DAO has approved the proposal, a group of Third Party managers will be assigned to operate with all of the Linked Wearables features.
Linked Wearables
Linked Wearables are regular wearables mapped to external NFTs. The 3D model version of your NFTs that will be used as in-world wearables will have to be compliant with the same guidelines as regular wearables.
To create a Linked Wearable, you will need to:
- Create a Linked Wearable Collection
- Upload you Wearables either in bulk or individually
We’ll be seeing how to work with Linked Wearables in the sections down below.
Creating a Linked Wearable Collection
Creating a Linked Wearable collection is the first step into creating our Linked Wearables.
Linked wearables are grouped in collections that can be created, edited and deleted by Third Party Managers. Each collection can contain an arbitrary number of Linked Wearables.
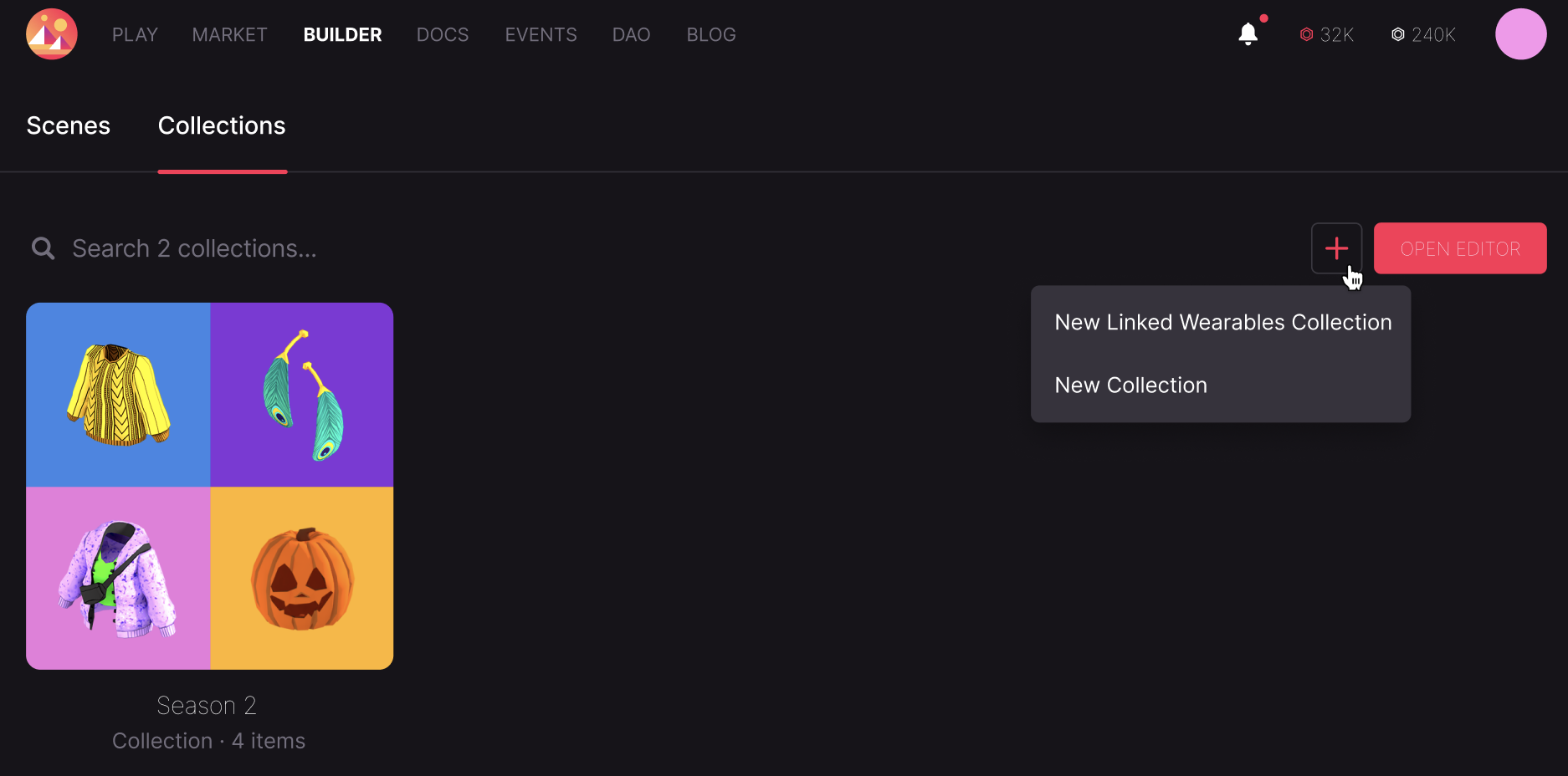
To create a new Linked Wearable follow these steps:
-
Create a new Linked Wearables Collection.
-
Choose a name for the collection and an ID.
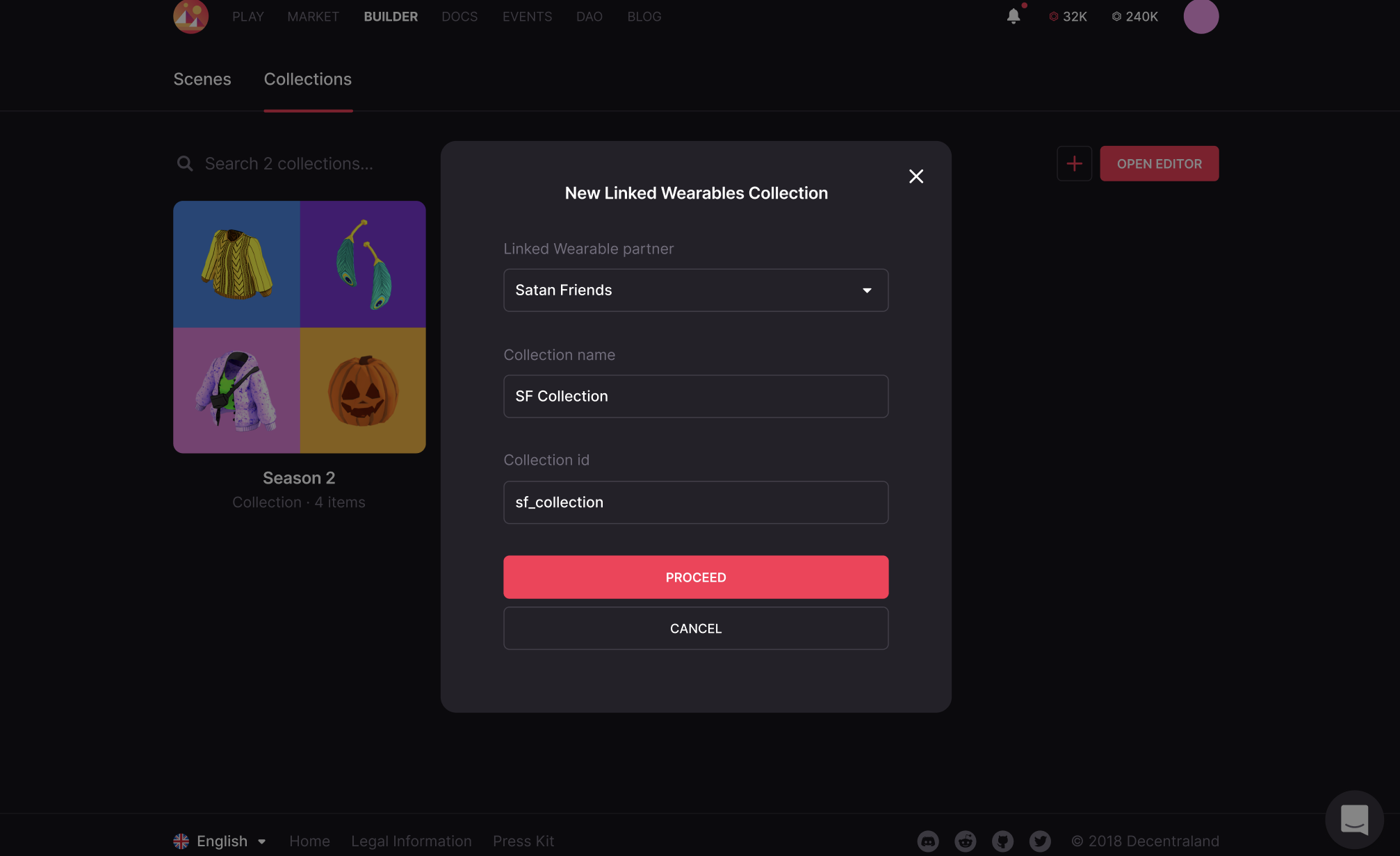
We strongly recommend that you choose a name that is unique and descriptive for the collection and as the ID or URN of the collection, the address of the NFT contract that will be mapped to the Linked Wearables. Using the NFT address as the ID of your collection will prove to be helpful when creating the API.
Creating Linked Wearables one by one
It’s possible to, as it already happens with standard wearables, upload your wearables’ 3D models one by one.
To do so, follow these steps:
-
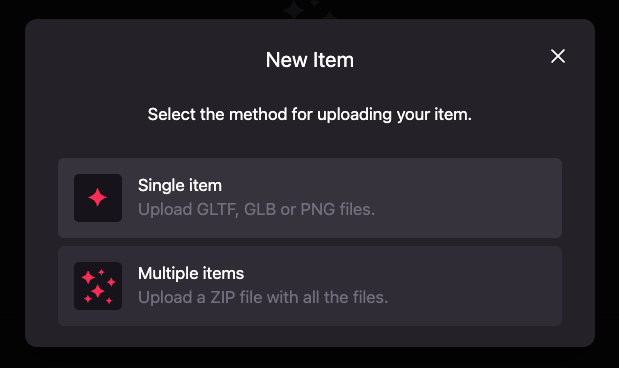
Click on the New items button.
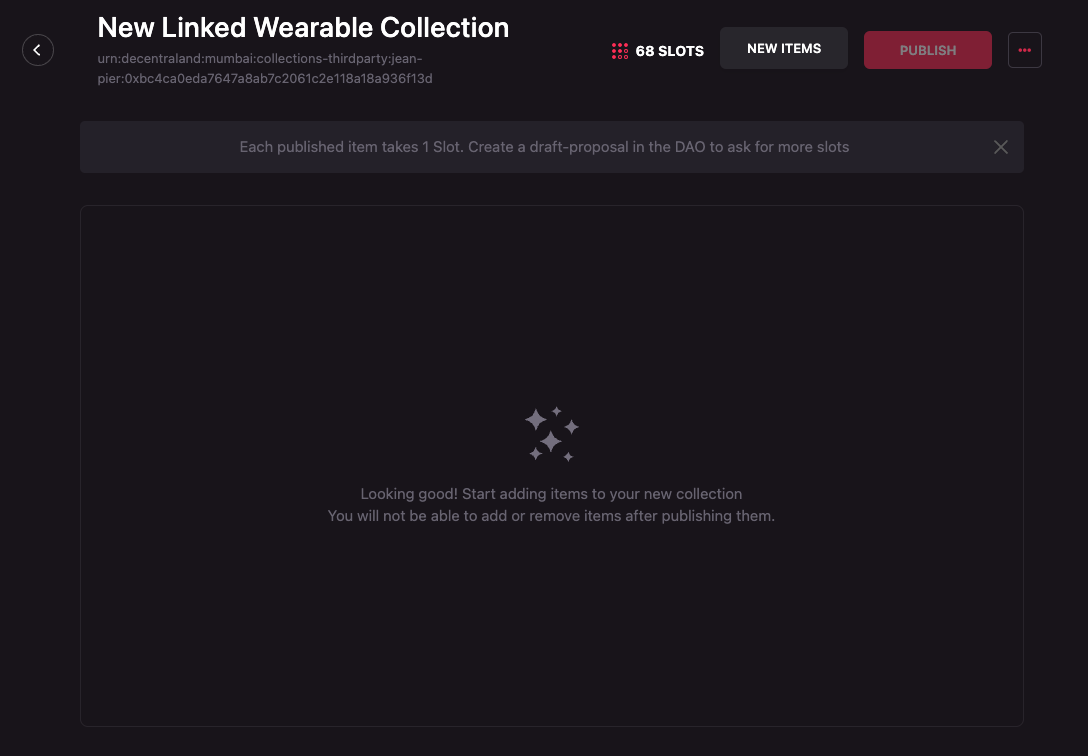
-
Select the Singe items option.
-
Follow the steps to upload and configure your wearable as it is described in the Uploading an item section in the wearables editor user guide.
Creating Linked Wearables in bulk
As Linked Wearable collections can contain a big number of items, it is possible to upload the 3D models and the information of the wearables in bulk.
The process of uploading wearables in bulk involves uploading a ZIP file for each wearable containing the following:
- The required 3D model files of the wearable (GLB, GLTFs, texture files, etc).
- A required
wearable.jsonfile containing the information of the wearable. - An optional
thumbnail.pngfile containing the thumbnail of the wearable that will be seen in the Builder and the world. If it is not provided, one will be generated using the 3D model.
The 3D models and the optional thumbnail.png follow the creating wearables guidelines and the wearables editor user guide on how to create a custom thumbnail.
The wearable.json accompanying the content of the wearables has the following format (typed as Typescript would):
type WearableConfiguration = {
/** The URN of the wearable */
id?: string
/** Name of the wearable */
name: string
/** Description of the wearable */
description?: string
data: {
/** Wearables to replace when equipping the wearable */
replaces: WearableCategory[]
/** Wearables to hide when equipping the wearable */
hides: WearableCategory[]
/** Tags to identify the wearable */
tags: string[]
/** Representations of the wearable */
representations: WearableRepresentation[]
/** Category of the wearable */
category: WearableCategory
}
}
type WearableRepresentation = {
/** Body shape of the representation */
bodyShapes: BodyShape[];
/** File path to the main file of the representation (GLB, GLTF, etc) */
mainFile: string;
/** A list of the file paths of the files that belong to the representation */
contents: string[];
/** Wearables to hide when equipping this representation */
overrideHides: WearableCategory[];
/** Wearables to replace when equipping this representation */
overrideReplaces: WearableCategory[];
}
enum WearableCategory = {
EYEBROWS = 'eyebrows',
EYES = 'eyes',
FACIAL_HAIR = 'facial_hair',
HAIR = 'hair',
HEAD = 'head',
BODY_SHAPE = 'body_shape',
MOUTH = 'mouth',
UPPER_BODY = 'upper_body',
LOWER_BODY = 'lower_body',
FEET = 'feet',
EARRING = 'earring',
EYEWEAR = 'eyewear',
HAT = 'hat',
HELMET = 'helmet',
MASK = 'mask',
TIARA = 'tiara',
TOP_HEAD = 'top_head',
SKIN = 'skin'
}
enum WearableBodyShape {
MALE = 'urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseMale',
FEMALE = 'urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseFemale'
}
Some things to consider about the wearable.json file:
- All the information about the wearable categories and which to choose can be found in the creating wearables guidelines.
- The
idfield is optional and can be used to:- Create a wearable with an specific ID.
- Update a wearable in Bulk (which will be seen in the Editing wearables in bulk
- The
idfield must contain the whole ID of the wearable, that is, the third party record id, the collection id and the item idurn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:third-party-id:collection-id:item-id. We recommend the id to be formed asurn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:third-party-id:contract-address:token-id, that is, if our wearable will be mapped to the token1in the NFT contract0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d, taking that into consideration, the URN for the example would beurn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:third-party-id:0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d:1. - The representations array will contain the information about how each body shape will look like. Each wearable MUST contain at least one representation (it can have one or the two of them), that is, taking
into consideration the body shapes that we currently have, either
urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseMaleorurn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseFemale. Each representation will describe which models will be used for each body shape.
The following is an example of a wearable.json file that contains a model for each body shape:
{
"id": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:third-party-id:0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d:1",
"name": "Special hat",
"description": "A description of the wearable",
"data": {
"replaces": [],
"hides": ["hair"],
"tags": ["special", "new", "hat"],
"representations": [
{
"bodyShapes": ["urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseMale"],
"mainFile": "aMaleModelFile.glb",
"contents": ["aMaleModelFile.glb", "aTextureFile.png"],
"overrideHides": [],
"overrideReplaces": []
},
{
"bodyShapes": ["urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseFemale"],
"mainFile": "aFemaleModelFile.glb",
"contents": ["aFemaleModelFile.glb", "anotherTextureFile.png"],
"overrideHides": [],
"overrideReplaces": []
}
],
"category": "hat"
}
}
This file will be zipped alongside the aMaleModelFile.glb, aTextureFile.png, aFemaleModelFile.glb and anotherTextureFile.png.
To add a custom thumbnail to the wearable, you can add a thumbnail.png file.
Once all the files are ready, to upload the wearables in bulk, follow these steps:
-
Click on the New items button.

-
Select the Multiple items option.

-
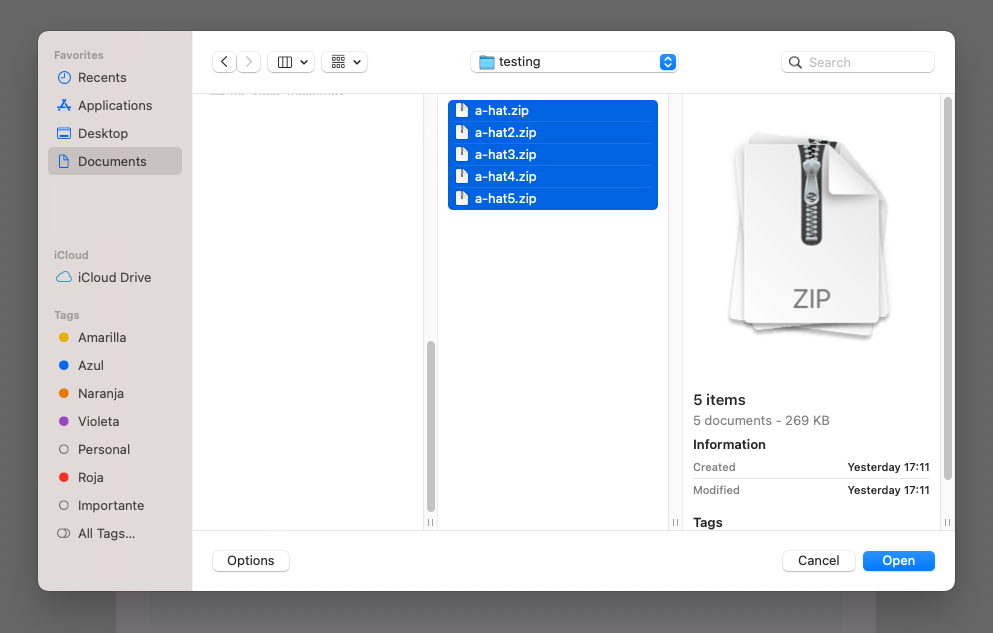
Click on the Browse yor computer link to open your file manager and elect all the zips containing your wearables.
-
Review if all the files are correct or if they need to be fixed. In this case, the model of the wearable isn’t set or the
wearable.jsonfile has an incorrectly set representation.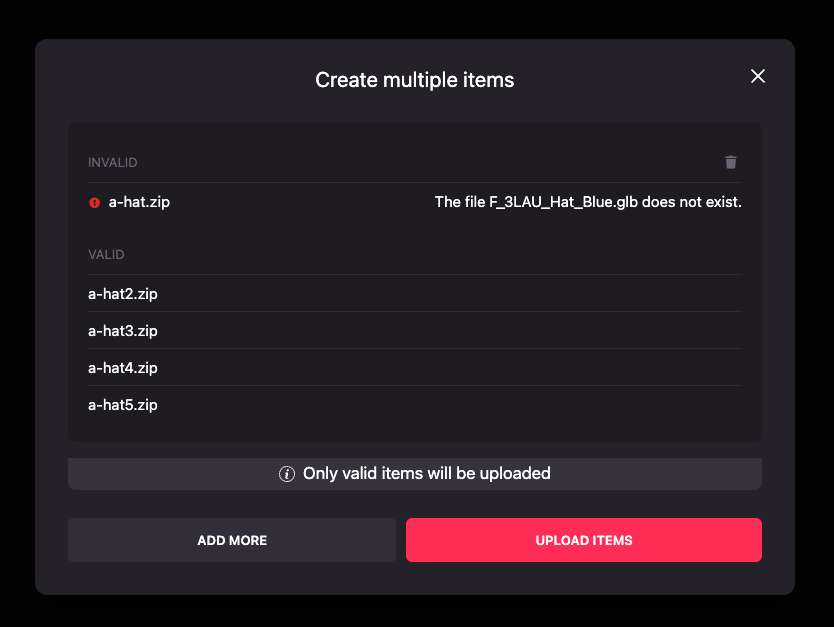
-
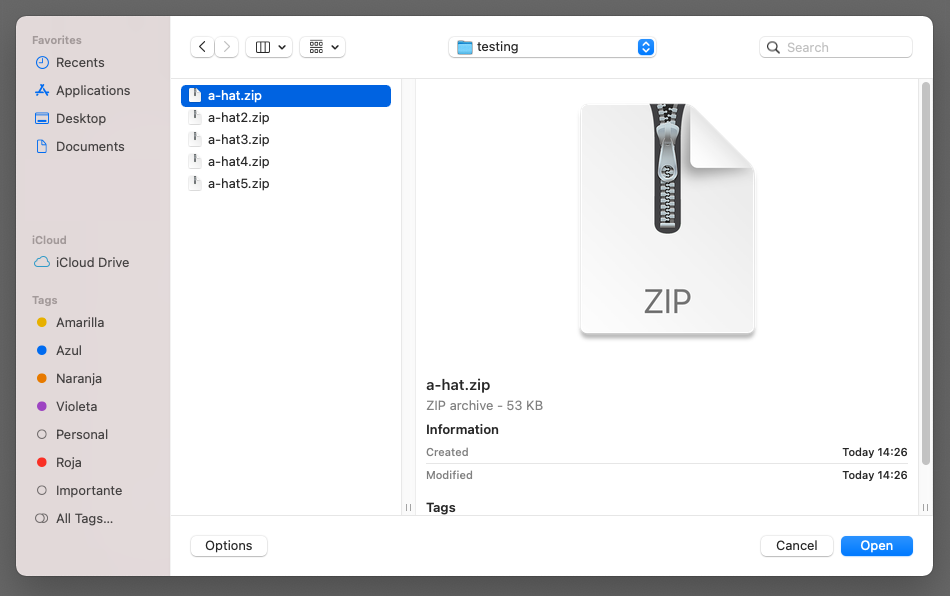
Fix any errors by clicking the Add more button and re-uploading the failed files with the same name or by dismissing the errors using the trash icon on the top right section of the modal.
-
Upload all wearables by clicking Upload items.
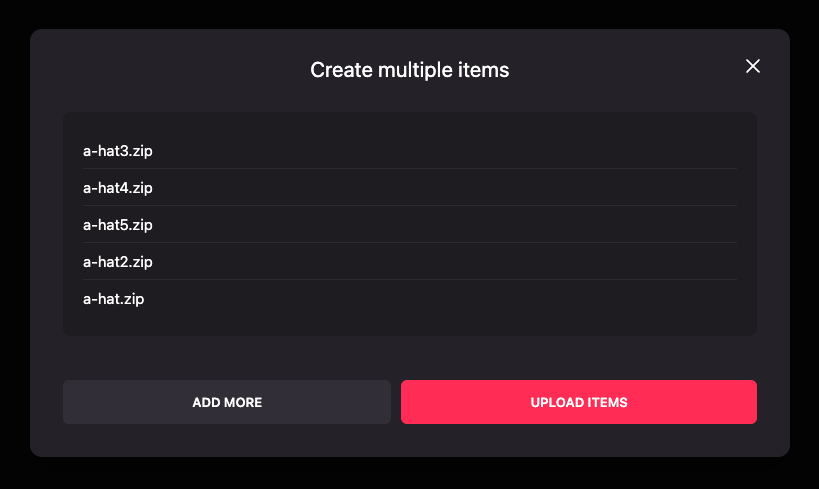
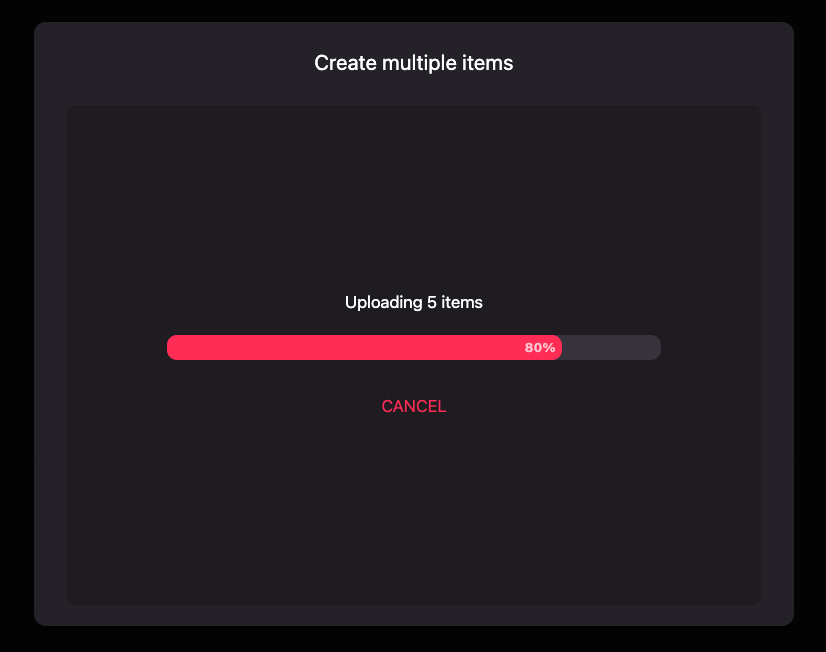
-
Be patient, this might take a while!
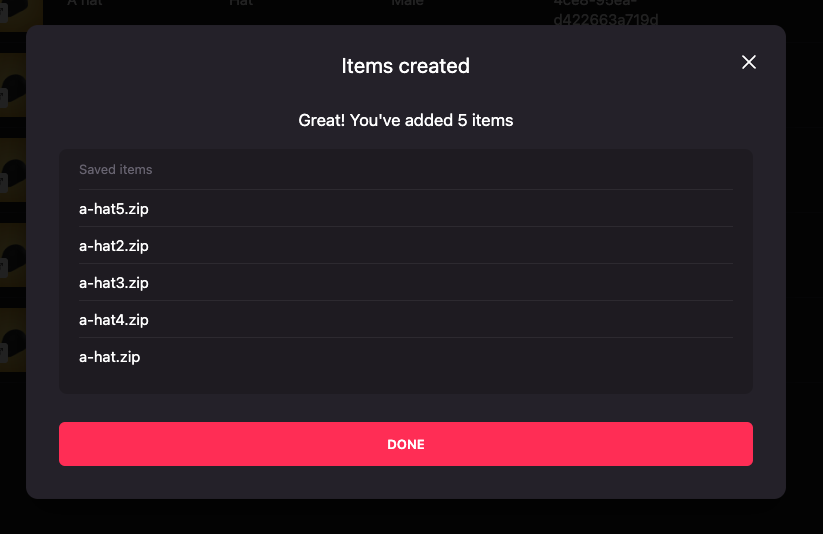
-
Success! Your items are now available in your collection.
Common errors that must be avoided when uploading batched items:
- The
idfield is set to a value that is already being used by another wearable. - The
idfield is set to a value that is not a valid ID. For example, the third party id or collection id belong to another third party or collection. - There’s no
wearable.jsonfile in the zip. - The ZIP file doesn’t have in its root directory the
wearable.jsonfile. - The
wearable.jsonhas an incorrect format or values. - The file is bigger than 2MBs. Linked Wearables have the same limitation as regular wearables in terms of size as the standard ones.
- The custom optional thumbnail image is not a png file.
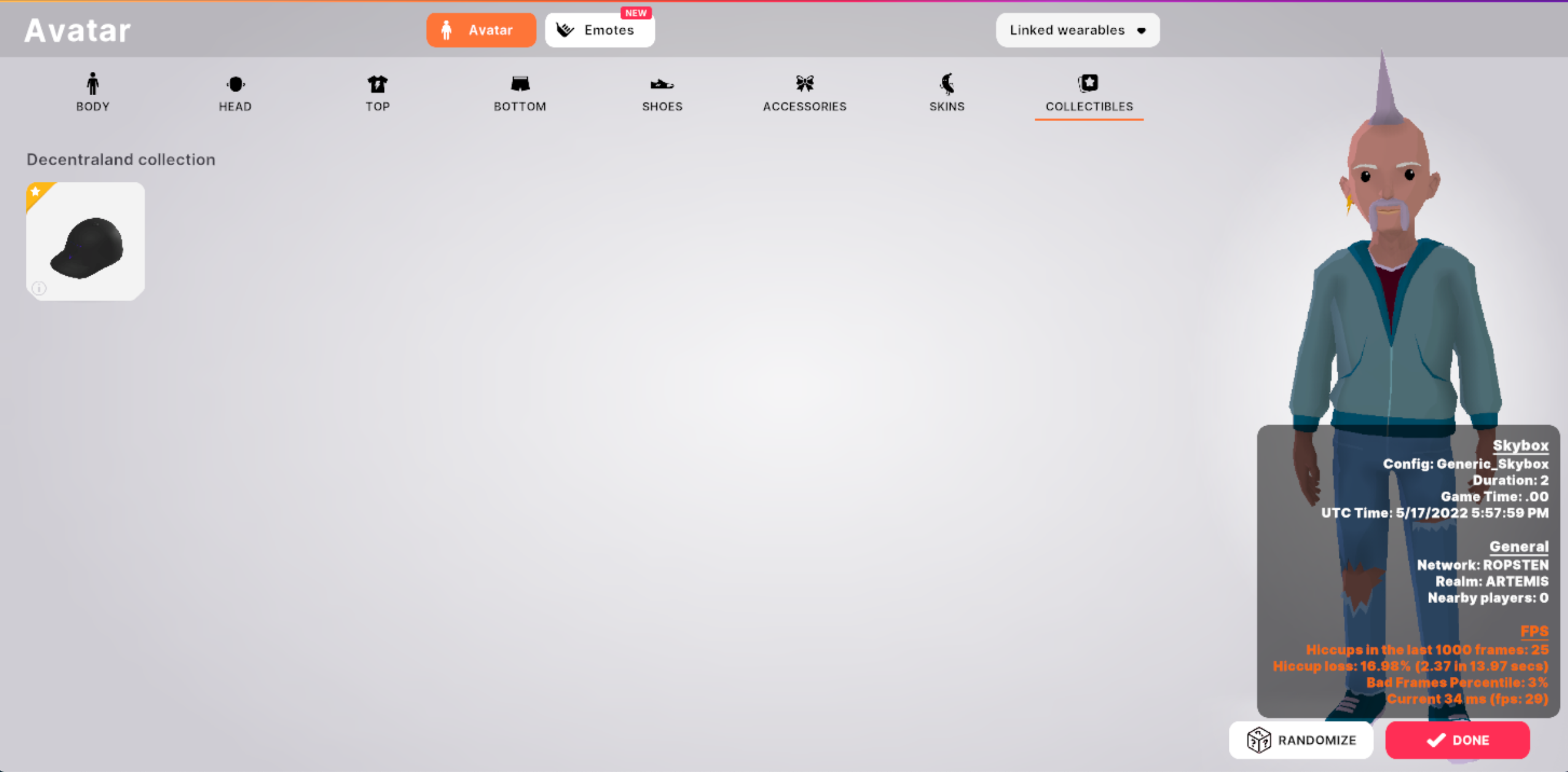
Seeing the wearables in world
Linked Wearables can be seen in world to review how the model will work once published and approved.
To be able to see a wearable in world, follow these steps:
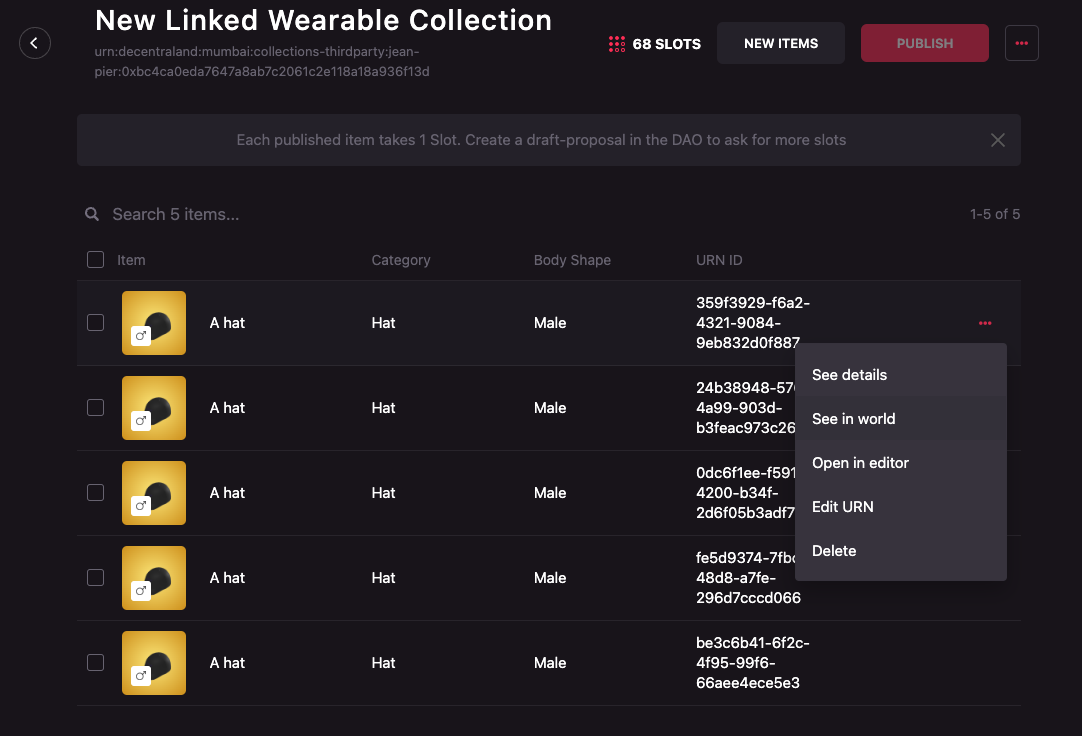
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the right of the item that you want to see in world. A dropdown will appear. Select See in world.
-
The Decentraland World will open. Navigate to your backpack to see the wearable.
Editing the collection name
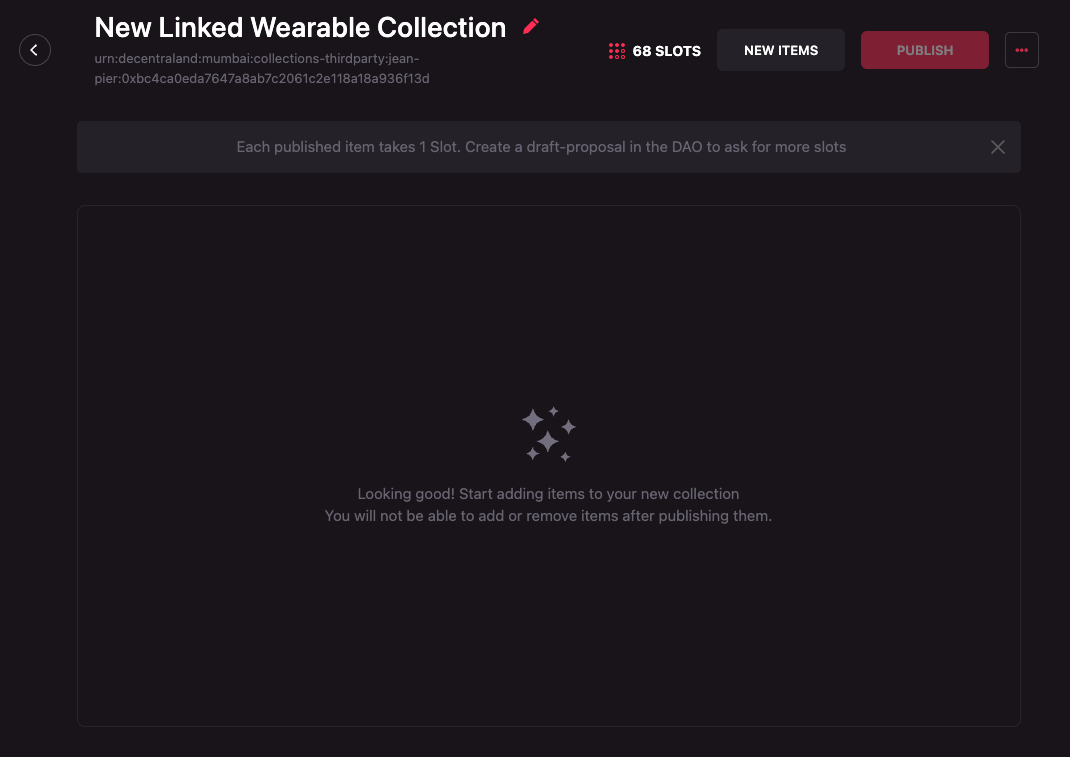
A collection can be renamed at any time by a Third Party manager.
To edit the name of a Linked Wearable Collection follow these steps:
-
Move the mouse over the collection name and click on the red pencil icon that appears on hover.
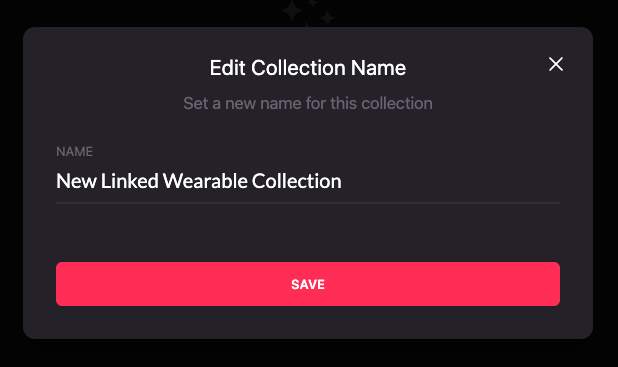
-
Choose a new name for the collection and click on the save button.
Editing the collection ID or URN
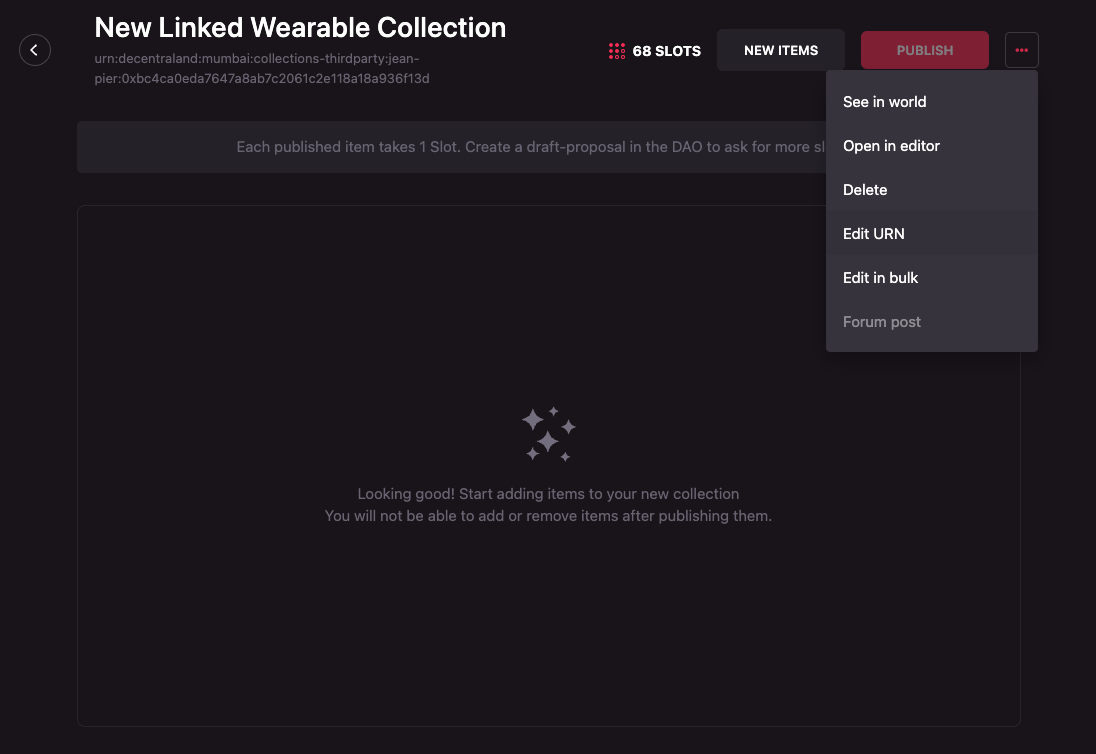
The collection’s ID or URN can be changed by a Third Party manager only if the collection has no published wearables.
To edit the ID or URN of a Linked Wearable Collection follow these steps:
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the far right of the set of buttons. A dropdown will appear. Select Edit URN.
-
Write the new ID or URN for the collection and click Save.
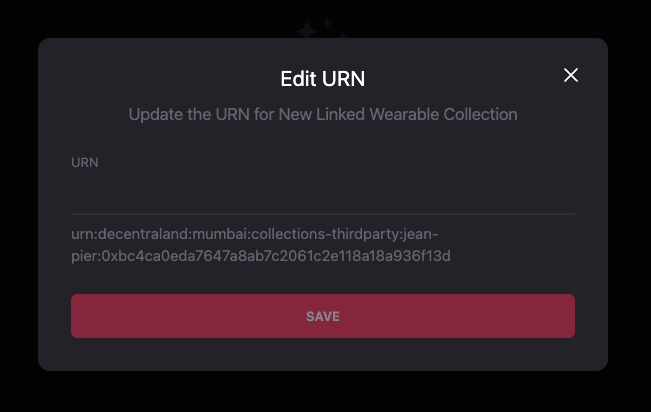
The ID or URN of the collection MUST be unique, changing it to an existent one will fail.
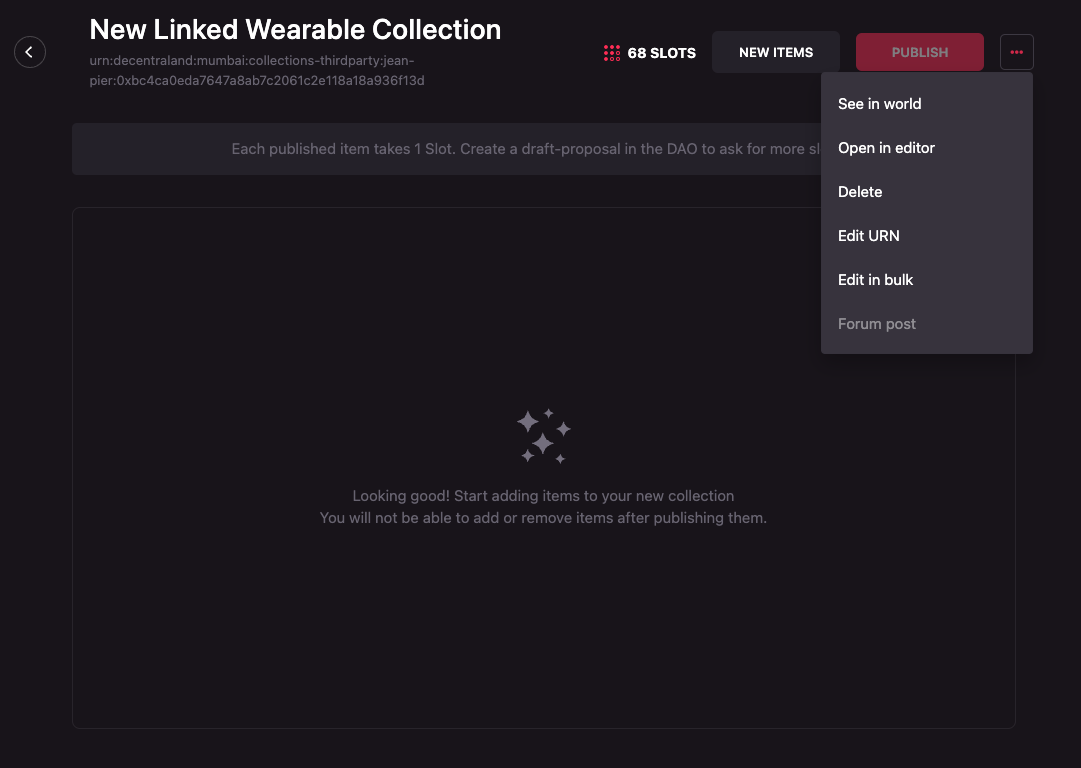
Deleting the collection
A collection can be delete by a Third Party manager only if the collection has no published wearables.
To delete Linked Wearable Collection follow these steps:
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the far right of the set of buttons. A dropdown will appear. Select Delete.
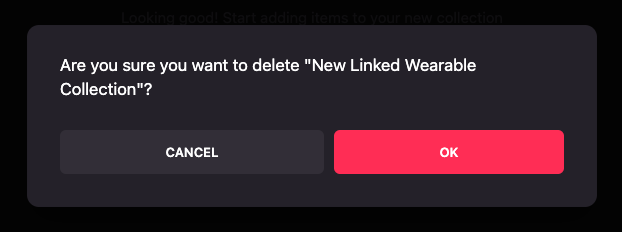
-
A Confirmation modal will appear, if you wish to proceed, click Ok, otherwise click on Cancel.
Editing a single wearable
To edit a single wearable, follow these steps:
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the right of the item that you want to see in world. A dropdown will appear. Select Open in editor.
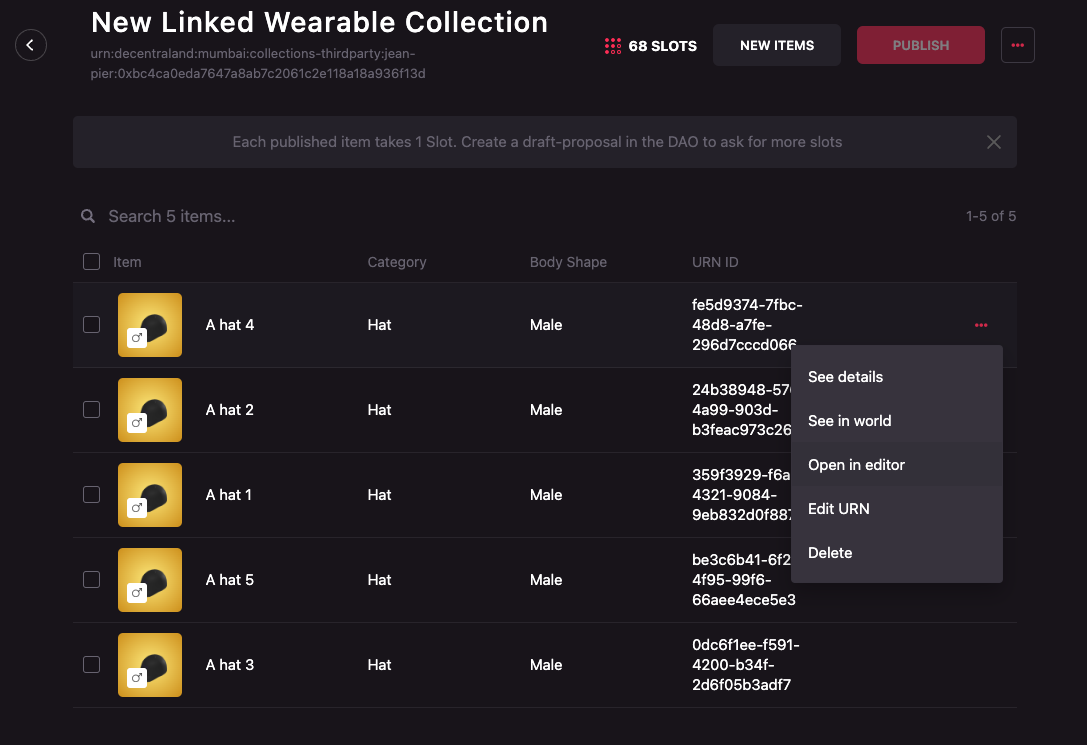
-
Edit the wearable as standard wearables are edited. Follow the Editing items section in the wearables editor user guide.
Editing a wearable’s ID or URN
Wearables can have their ID or URN changed manually by following the steps below:
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the right of the item that you want to see in world. A dropdown will appear. Select Edit URN.
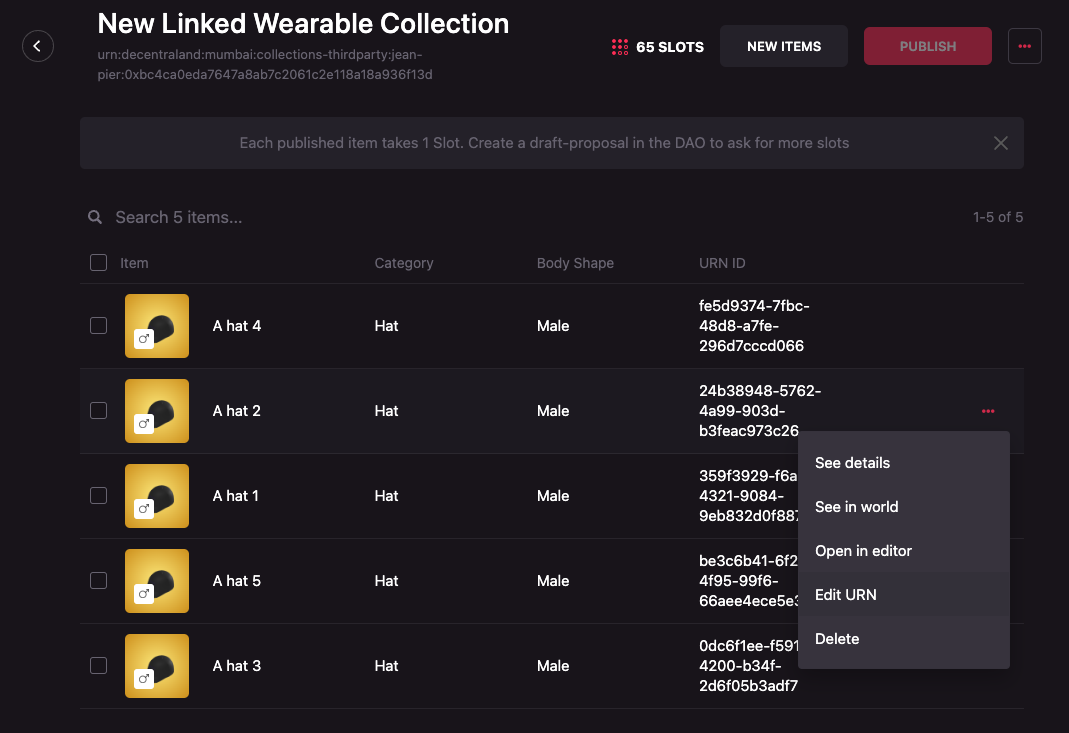
-
Use the Edit URN modal to write the new URN.
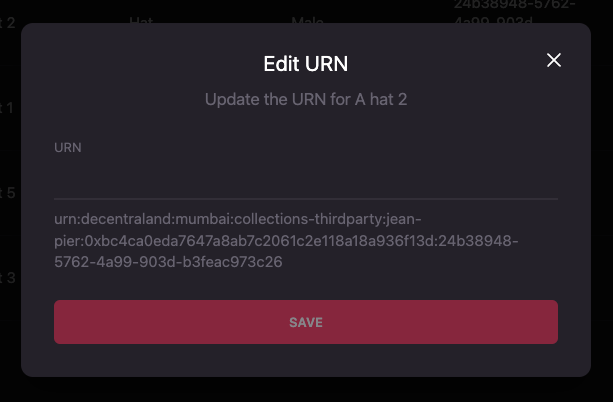
To consider when updating the ID or URN of a wearable:
- The input will receive only the ID for the wearable.
- The ID can’t be repeated in the same collection.
- We recommend the ID of the wearable to be the same as the token ID of the NFT it will be mapped to.
Editing wearables in bulk
Following the same idea previously seen in the Creating wearables in bulk section, third party managers can make changes to the wearables in bulk.
To make changes in bulk to wearables, it is necessary to create a ZIP file for each of the wearables that will be changed.
These ZIP files must be created following the format described in Creating wearables in bulk with one exception, in the wearable.json file, the id
property MUST be set to the id or URN of the wearable that will be changed. This is mandatory as it’s the only way to identify the wearable to be changed.
Taking into consideration the example in the Creating wearables in bulk section, if we would like to change some of the properties of a wearable, for example,
the name where we forgot to add a number to it, we should include a wearable.json file in the zip as the next example:
{
"id": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:third-party-id:0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d:1",
"name": "A hat 1",
"description": "A description of the wearable",
"data": {
"replaces": [],
"hides": ["hair"],
"tags": ["special", "new", "hat"],
"representations": [
{
"bodyShapes": ["urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseMale"],
"mainFile": "aMaleModelFile.glb",
"contents": ["aMaleModelFile.glb", "aTextureFile.png"],
"overrideHides": [],
"overrideReplaces": []
},
{
"bodyShapes": ["urn:decentraland:off-chain:base-avatars:BaseFemale"],
"mainFile": "aFemaleModelFile.glb",
"contents": ["aFemaleModelFile.glb", "anotherTextureFile.png"],
"overrideHides": [],
"overrideReplaces": []
}
],
"category": "hat"
}
}
Where the id field is set to the id or URN of the wearable that will be changed and the name field is set to the new name of the wearable.
Once the ZIP files are ready, follow these steps to edit the items in bulk:
-
Click on the meatballs menu (three horizontal dots) on the far right of the set of buttons. A dropdown will appear. Select Edit in bulk.
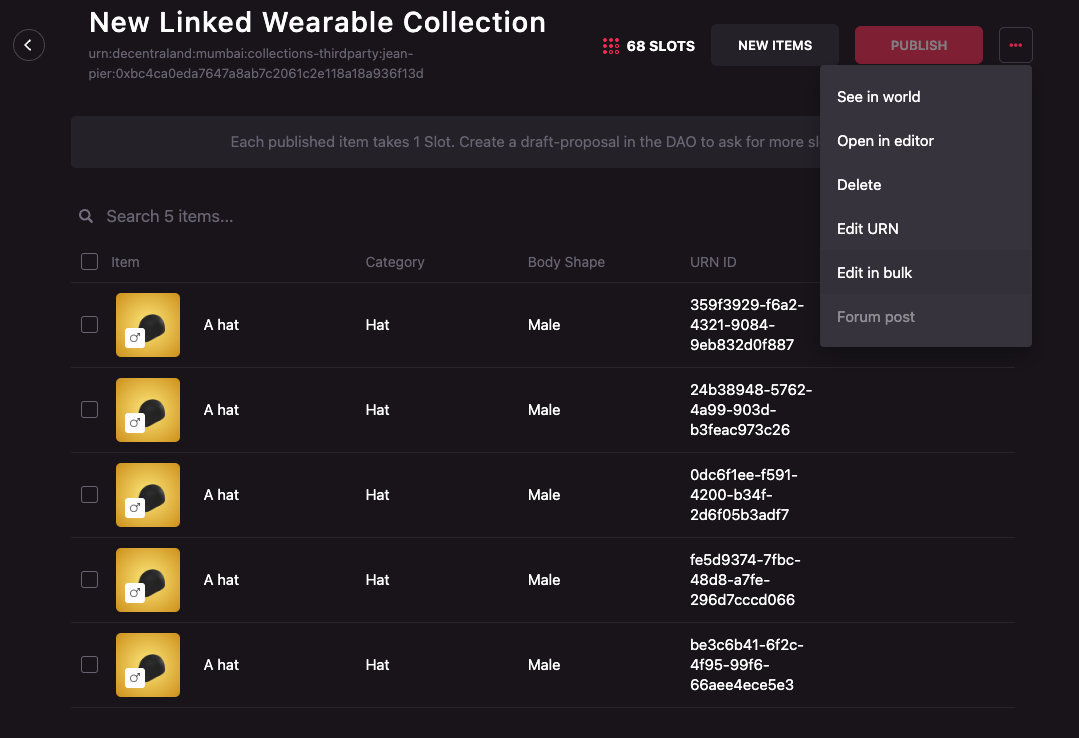
-
A modal similar to de one in the Uploading models in bulk will appear. Click on the Browse your computer link to open your file manager.
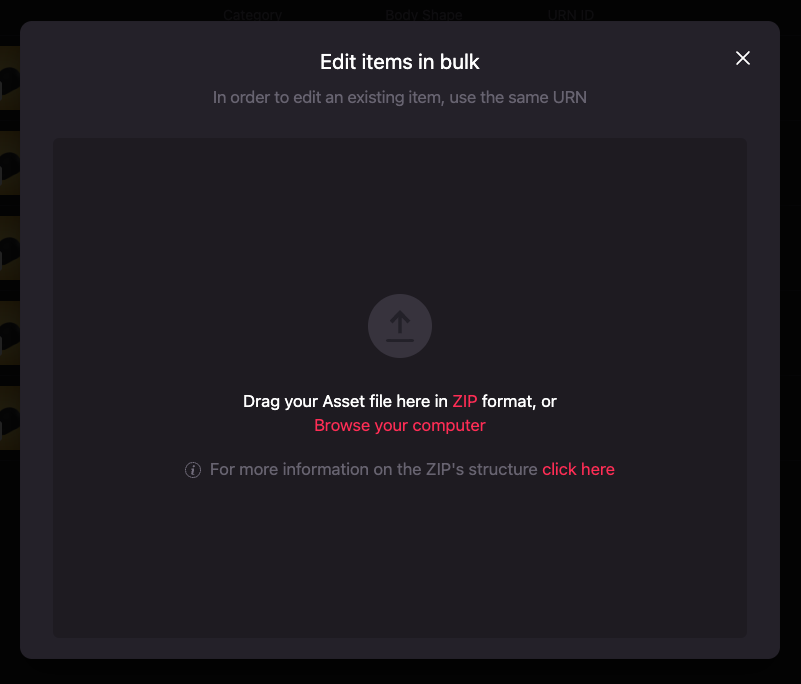
-
Select all the ZIP files of the items that will be edited.

-
Review if all the files are correct or if they need to be fixed. In this case, the model of the wearable isn’t set or the
wearable.jsonfile has an incorrectly set representation.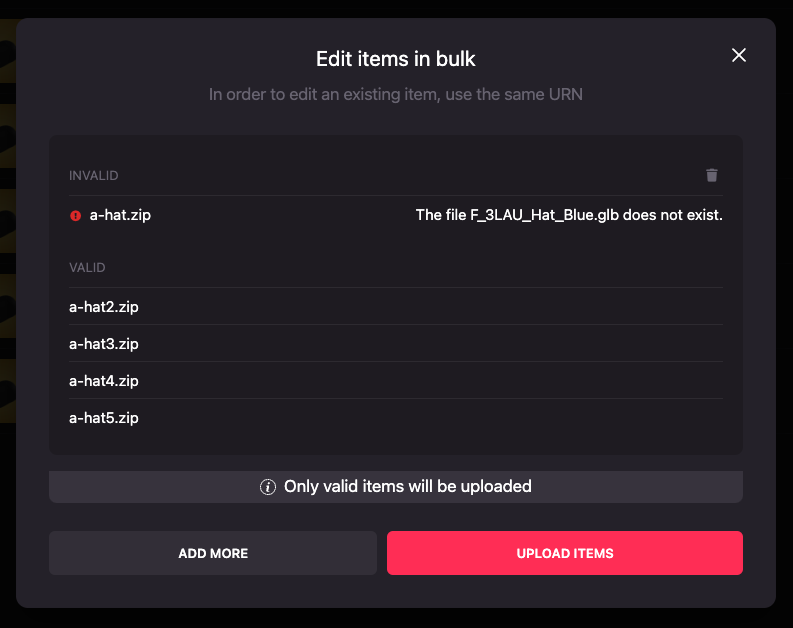
-
Fix any errors by clicking the Add more button and re-uploading the failed files with the same name or by dismissing the errors using the trash icon on the top right section of the modal.

-
Upload all wearables by clicking Upload items.
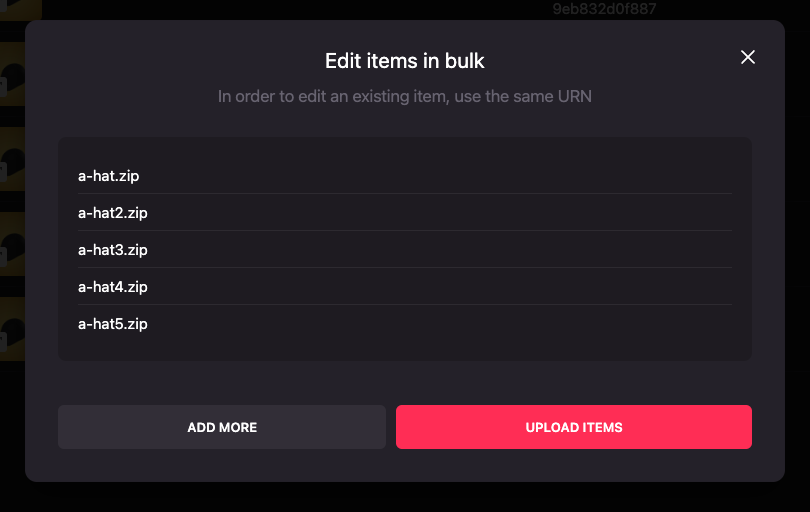
-
Be patient, this might take a while!
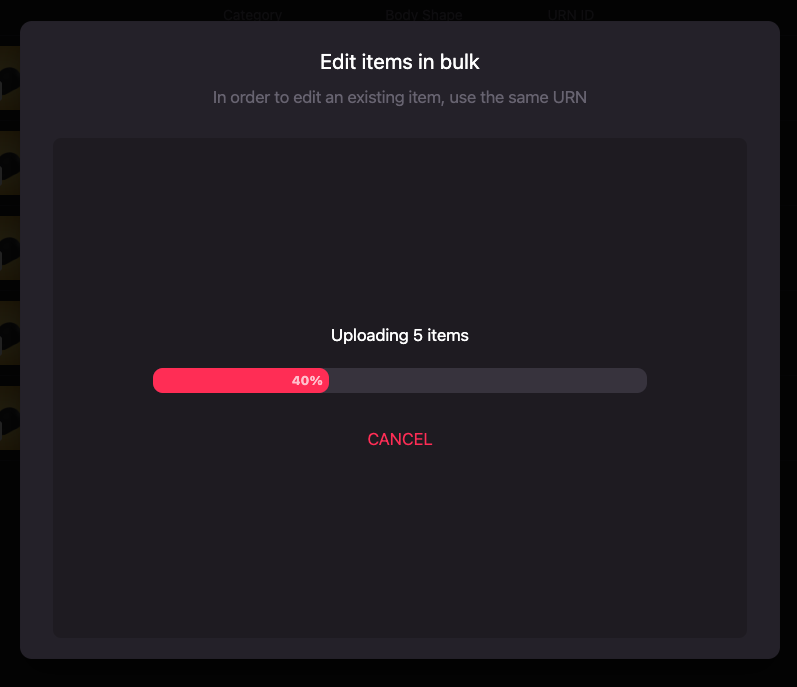
-
Success! Your items are now available in your collection.
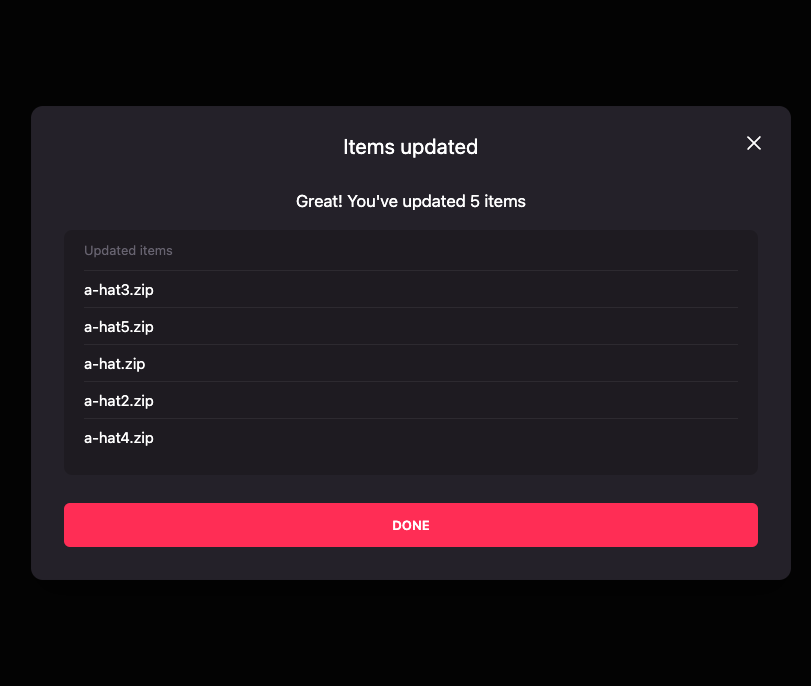
Submitting your Linked Wearables
Your Linked Wearables need to go through a publishing and curation process as the regular wearables do. Although the publication and curation process is not the same as the one for the regular wearables, it keeps the same steps, all items must be first be published to later be curated by an assigned curator.
The following sections will show you how to publish your Linked Wearables to be curated.
Publishing wearables
Once your wearables are ready, they must be published for curation. Your wearables are published in groups of items, you can choose which items are ready to be curated
by selecting them and clicking the Publish button. A slot per wearables will be consumed upon publishing and the third party managers won’t be able to publish any
more wearables until the ones that are already published are curated.
To publish your wearables, you need to:
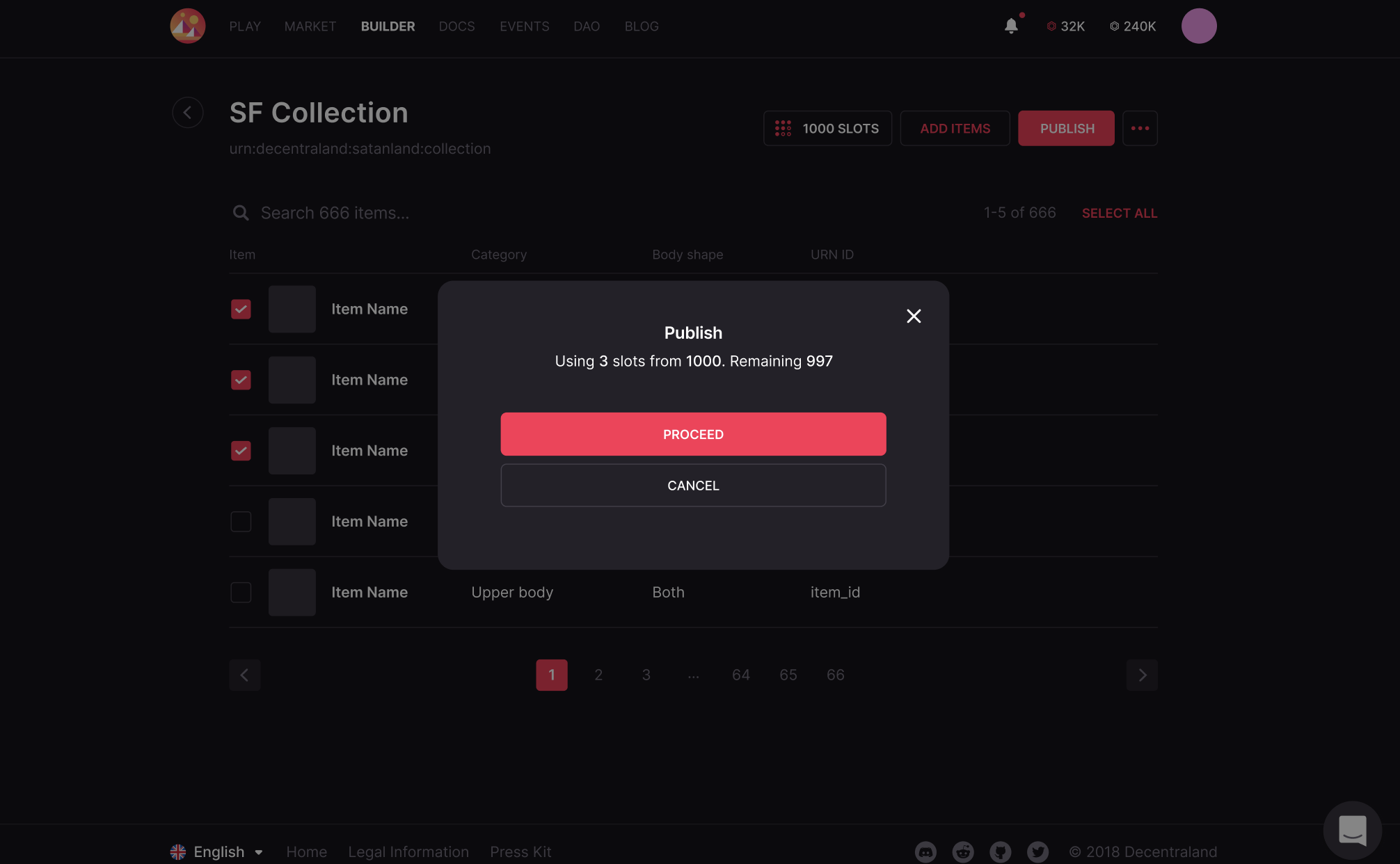
-
Select the items to be published and wait for the Curators Committee to approve them
Curation
As with regular wearables, your 3D models will need to get the Curators Committee’s approval. You are not excluded from this rule as Decentraland’s aesthetic and gameplay still needs to be safe guarded.
The curation process will differ according to the process used to generate the wearables. Linked Wearables collections admit handcrafted and programmatically generated wearables.
Handcrafted wearables
For 3D models that were made individually without any automated process (the usual method for most regular wearables) the Curator will need to go through all items in the collection individually to make sure they are all compliant with the Wearable Guidelines.
Programmatic collections
Your collection is a Programmatic Collection if each 3D model was not crafted individually by hand, but automatically generated with code, many times from traits that were previously designed and modeled. For example: CryptoPunks and BAYC are examples of 2D pfp NFT Collections that were created programmatically.
Third Parties that make a collection for Linked Wearables programmatically (3D models to upload), will need to include this information in their Linked Wearables Registry proposal.
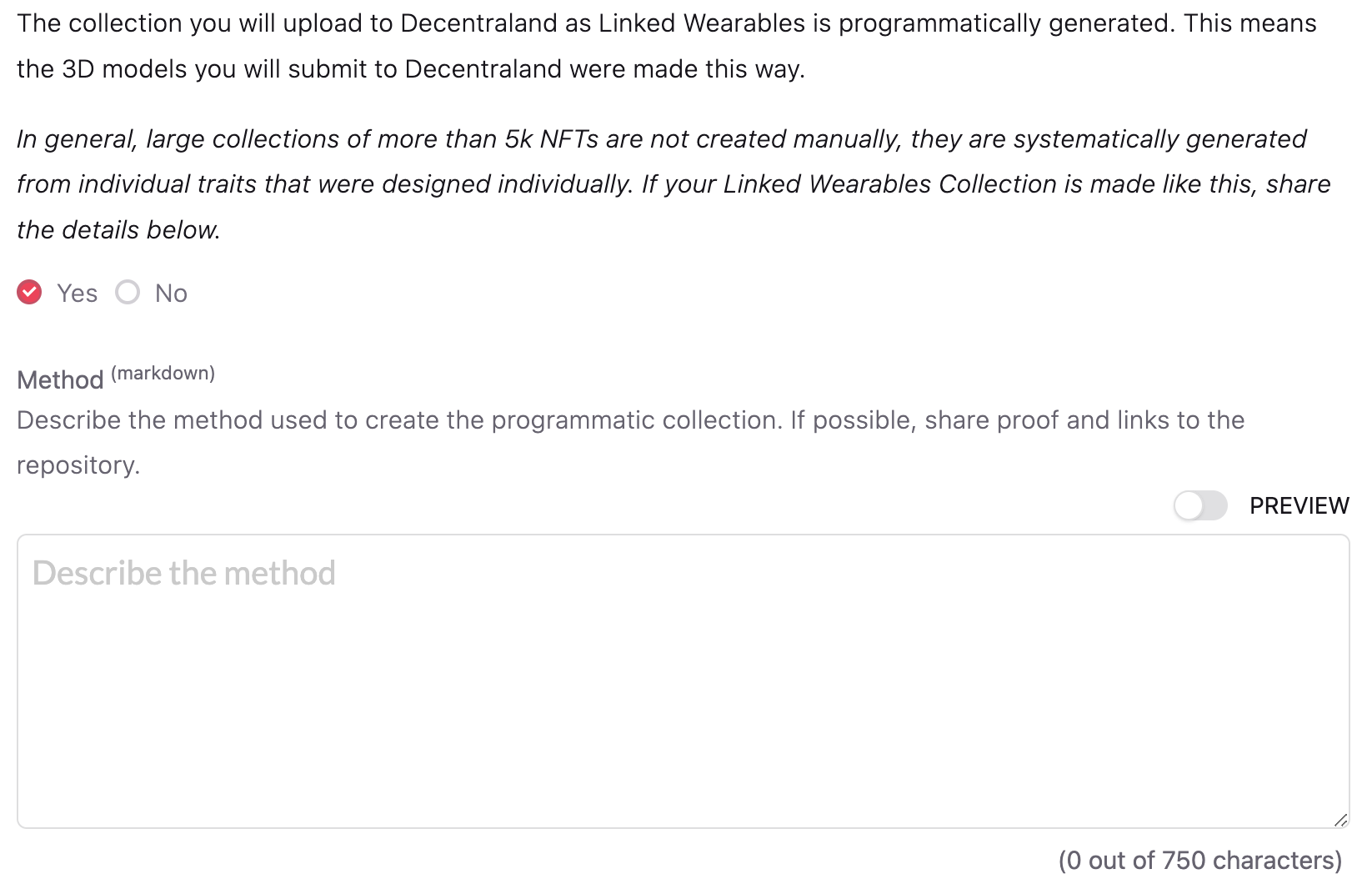
For programmatic collections, not all items have to be curated individually. The number of items to be curated in each collection depends on the collection’s size, this was defined by the DAO in this proposal.
Building the API
In order for Linked Wearables to work, the third parties need to provide an API that will be queried by the Decentraland services (Catalyst) with 2 endpoints:
-
@GET /registry/:registry-id/address/:address/assets- Retrieves a list of assets associated with a given address. -
@GET /registry/:registry-id/address/:address/assets/:id- Validates if a DCL asset is owned by a user. -
@GET /registry/:registry-id/owners-bloom-filter- Retrieves a bloom filter as an hex value comprising all the owners a registry has.
Technical details and examples here.
In the next sub-sections we’ll provide an explanation on how to build the mentioned API by using an implementation example of the many possible ones.
Endpoint @GET /registry/:registry-id/address/:address/assets
If you’ve followed the steps to create a new collection and the steps to either edit the item’s id or URN or to create items in bulk, you already have:
- Created a collection which its ID or URN is the contract address of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
- Created wearables which IDs or URNs are the token ids of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
By doing this, you can query your NFT contract or indexer to build the information required to respond to the API as it contains the information about who owns which wearable:
Let’s say your contract implements the ERC721 standard with the enumeration extension. If we would like to get the tokens owned by the
address 0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942, your API can query (as one of the sources) the contract using the balanceOf to get the amount of tokens owned by the address and later loop the tokens with the tokenOfOwnerByIndex to get the information about the tokens the address has.
Having all the tokens that an address owns, the API can easily build the response by mapping each of the assets:
{
"id": "0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:0",
"amount": 1,
"urn": {
"decentraland": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:cryptohats:0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:0"
}
}
The id property will be set to the contract_address:token_id of each of the retrieved tokens, the amount to 1 and the urn property will be set to have the
decentraland property with the value urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:registry_id:contract_address:token_id, where the registry_id and contract_address can be retrieved
from the query itself (contract_address must be previously set in the code) and the other values from the contract.
As an example, by querying the API to get the assets owned by 0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942:
curl https://api.cryptohats.io/registry/cryptohats/address/0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942/assets
The API can do the following:
- Query the contract
0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cddwith the user’s address by usingbalanceOf(0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942), retrieving the amount of tokens owned by the user, in this case, 2. - Query the contract
0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cddtwo timestokenOfOwnerByIndex(0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942, 0),tokenOfOwnerByIndex(0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942, 1)returning the token ids 58 and 59. - Respond with:
{
"address": "0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942",
"assets": [
{
"id": "0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:58",
"amount": 1,
"urn": {
"decentraland": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:cryptohats:0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:58"
}
},
{
"id": "0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:59",
"amount": 1,
"urn": {
"decentraland": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:cryptohats:0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:59"
}
}
],
"total": 2,
"page": 1,
"next": "https://....&startAt=1234"
}
Endpoint @GET /registry/:registry-id/address/:address/assets/:id
If you’ve followed the steps to create a new collection and the steps to either edit the item’s id or URN or to create items in bulk, you already have:
- Created a collection whose ID or URN is the contract address of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
- Created wearables whose IDs or URNs are the token ids of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
By doing this, you can query your NFT contract or indexer to build the information required to respond to the API as it contains the information about who owns which wearable:
Let’s say your contract implements the ERC721 standard and you’re asked to retrieve information about an asset with an id if the asset is owned by an address.
By querying the contract using the ownerOf method, as we can extract the token id from the asset it because of the requirements assumed above (contract_address:token_id), it is possible to get the address of the owner of the token and, if it matches, respond with the required information about the asset.
As an example, by querying the API to get the information about the asset with id 0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:1 owned by the 0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942 address:
curl https://api.cryptohats.io/registry/cryptohats/address/0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942/assets/0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:1
The API can do the following:
- Query the contract
0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cddretrieved from the query by splitting the asset id by:, with the user’s address also retrieved from the query, by using the methodownerOf(1)that will return the address0x0f5d2fb29fb7d3cfee444a200298f468908cc942if the asset is owned by the user. - Respond with:
{
"id": "0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:1",
"amount": 1,
"urn": {
"decentraland": "urn:decentraland:matic:collections-thirdparty:cryptohats:0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd:1"
}
}
Endpoint @GET /registry/:registry-id/owners-bloom-filter
If you’ve followed the steps to create a new collection and the steps to either edit the item’s id or URN or to create items in bulk, you already have:
- Created a collection whose ID or URN is the contract address of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
- Created wearables whose IDs or URNs are the token ids of the NFTs that will represent or map to the Linked Wearables.
By doing this, you can query your NFT contract or indexer to build the information required to respond to the API as it contains the information about who owns which wearable:
Let’s say your contract implements the ERC721 standard and you used an indexer like TheGraph to make it’s data easily queriable using GraphQL. You’re then asked to retrieve a bloom filter which has all the addresses (owners) the registry has.
By using TheGraph, you could have an entity called Asset which has an owner property. That would allow you to return all assets owners by using the public GraphQL API TheGraph provides.
As an example, by querying the API to get the bloom filter for a registry:
curl https://api.cryptohats.io/registry/cryptohats/owners-bloom-filter
The API can do the following:
- Query TheGraph to get all the assets, selecting the owner property
assets {
owner
}
this will return something like this:
{
"data": {
"assets": [
{ "owner": "0xc04528c14c8ffd84c7c1fb6719b4a89853035cdd" },
{ "owner": "0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d" },
{ "owner": "0x1f0880e0b4514dc58e68b9be91693bfa8c067ac1" }
]
}
}
- For each owner add it to a BloomFilter and get an hex value. You can use an implementation like the one found on @ethereum/vm
import Bloom from "@ethereumjs/vm/dist/bloom"
const filter = new Bloom()
for (const owner of owners) {
filter.add(owner)
}
const data = filter.bitvector.toString("hex")
- Respond with:
{
"data": "00100000000000000000000000000000080010000800000000000000000000000080000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002000000000004000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000400000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000800000000040000000000000000000000000000020000000000000280000000000000000000000000000200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040040000000000000000000000000000000010000000000000000000000000000"
}
Important notice and considerations
The examples provided above on how to build the API are just examples, it’s not required to follow them. The implementations of the API can vary completely, for example, the information can be retrieved from different sources (an indexer like TheGraph, a Database previously populated or multiple indexers or contracts) and a NFT can be mapped to multiple decentraland wearables instead of having a 1:1 mapping with the NFTs.
Note that the URNs in the examples use matic for the protocol. This means that the third party registry smart contract has been deployed in the Matic network BUT it is not related to or limiting where your project can be created. Every urn for linked wearables items will use matic as the protocol. Remember that linked wearables work for any NFT project created at any EVM compatible network (Ethereum, Polygon, Binance Smart Chain, etc). So, if your project has been created in Ethereum, the urn of the item will have matic in the protocol and it is ok.
The purpose of the API is to map an owner of an NFT with a wearable (or multiple wearables) submitted to Decentraland and this mapping is done through the ID or URN of the wearable which can be found on each item detail page:
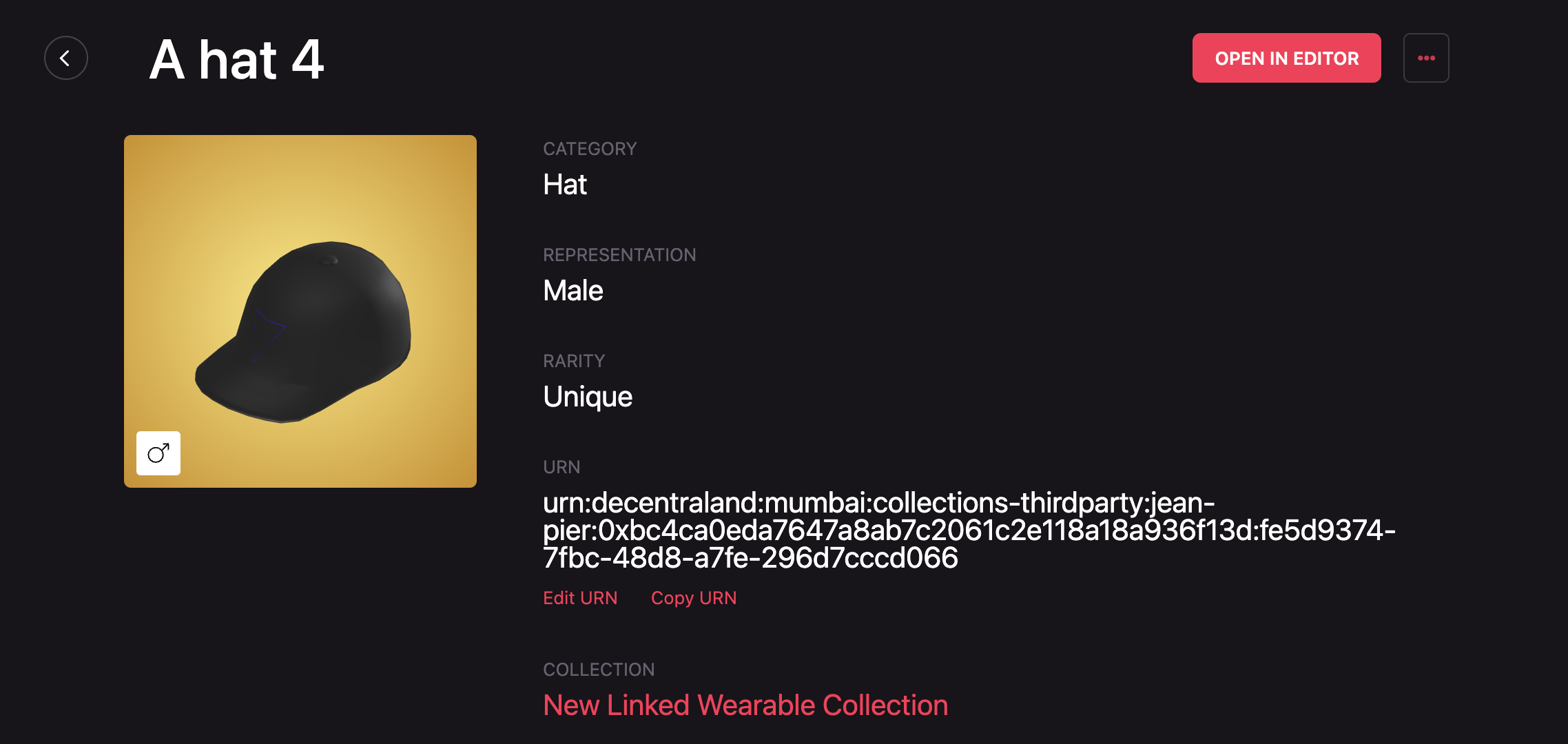
Closing up
Summary
These are the steps that Third Parties need to follow, in summary:
-
Create a DAO proposal in the category “Linked Wearables Registry”. You’ll need to:
- Request to be added to the Linked Wearables Registry
- Describe your company or community
- Describe your collection and the number of NFTs in it
- Define Managers
- Wait one week for DAO’s approval. Ask your community for help! they can vote for you to be accepted. Remember that MANA, Names, Lands, and/or Estates are needed to vote in the DAO.
-
Submit your linked wearables in the Builder using your available Slots.
- Create a linked wearable collection. We recommend using as its ID or URN the contract address of the NFTs that will represent or be mapped to the Linked Wearables.
- Create or upload your wearables either by uploading them one by one or in bulk.
- Use the URN of the wearables in the Builder to build your API. We recommend that your URN or ID to be set as the token id of the NFT that will be represented by the wearable.
- Build the API.
- Wait for the Curators Committee to approve the items in your collection.
- Spread the word! Tell your community that they can enjoy their brand new Linked Wearables in Decentraland!
Additional comments
- The DAO is the authority that will approve the addition of new Third Parties on the Linked Wearables Registry.
- The Curation Committee always has the power to reject specific items or all items within a collection.
- Linked Wearables work with any NFT project running at any blockchain, if the API provided can match the user address with the 3D model to show as Linked Wearable.